Artificial intelligence has been creeping into development workflows for years, but most tools still behave like glorified autocompleters. When Google unveiled Antigravity alongside its Gemini 3 launch on 18 November 2025, I was intrigued.
The company pitched it as an agent‑first development environment designed to offload more than just line‑by‑line coding. It promises autonomous agents that can edit files, run commands, and test applications, all while documenting their work with human-readable artifacts.
Rather than passively generating snippets, Antigravity aims to orchestrate entire tasks across the editor, terminal, and browser. I decided to spend a week using it as my primary IDE to see whether it lives up to the hype and how it compares with existing AI coding tools.
In this article…
What Is Google Antigravity?
Google Antigravity is a free, cross‑platform IDE built on a fork of Visual Studio Code. It integrates Gemini 3 Pro by default but can also run Anthropic’s Claude Sonnet 4.5 and an open‑source GPT model, giving users a choice of language models.
The platform’s defining feature is its agent‑first architecture: instead of a single assistant suggesting code, developers spawn autonomous agents that can plan, write, debug, and verify code across multiple surfaces.
These agents operate within the familiar IDE, but they also have a Manager View that functions like mission control, allowing you to coordinate several agents simultaneously.
Google emphasizes four guiding principles—trust, autonomy, feedback, and self-improvement. To earn users’ trust, each agent produces Artifacts—Markdown documents containing task lists, plans, test results, screenshots, and browser recordings—so you can verify what the AI has done.
Feedback is built into every surface: you can annotate an Artifact or a code segment with inline comments, and the agent will incorporate that feedback without halting its work. Finally, agents maintain a knowledge base, retaining snippets and lessons from past sessions.
Also Read: Google Gemini 2.5 vs GPT-4: Which AI Model Should You Choose in 2026?
Setup and Onboarding
Google Antigravity installer is available for Windows, macOS, and Linux. After downloading the application, you sign in with a Google account and choose your default model.
In my experience, the Mac version was stable, but some users have reported that the early Windows build occasionally crashes.
Once inside, Antigravity resembles VS Code with a side panel for agents. The Editor View looks familiar, complete with syntax highlighting, version‑control integration, and a terminal.
The Manager View opens a dashboard showing your active agents, their statuses, and their latest Artifacts. This split interface underscores Google’s vision: you can develop normally or step back and orchestrate agents at a higher level.
Google Antigravity User Interface and Workflow
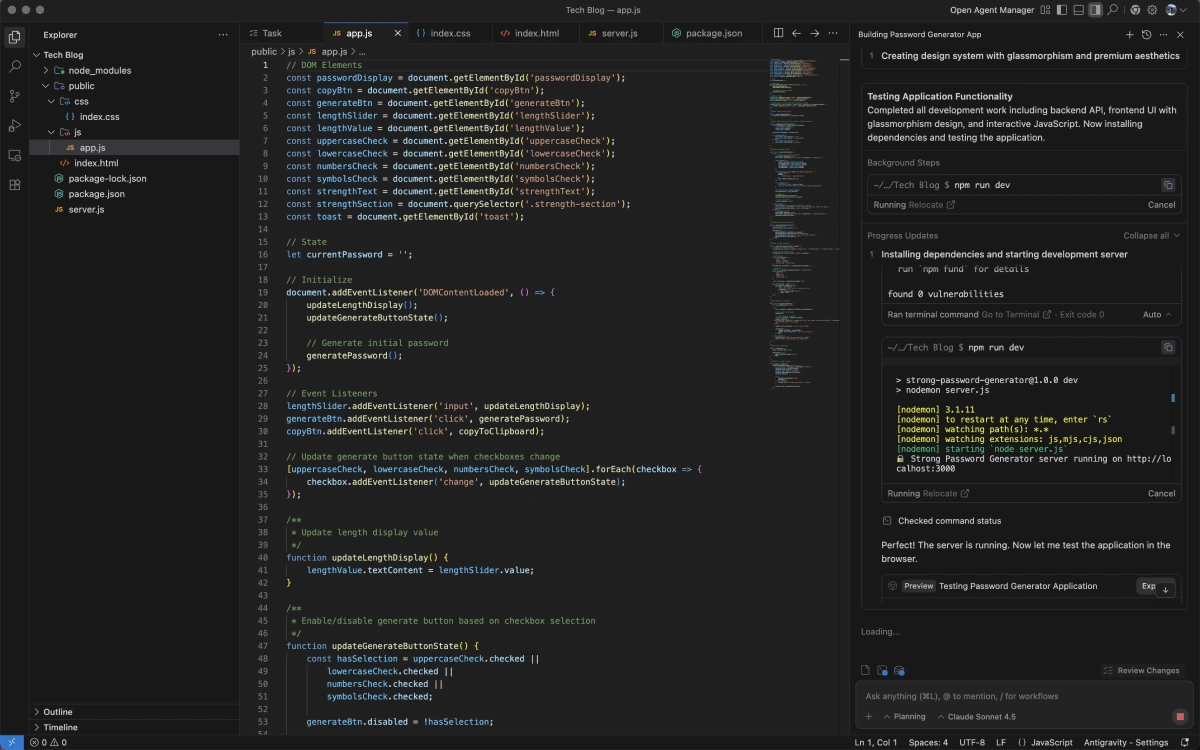
Dual Workspaces: Editor vs. Manager
Antigravity’s Editor View functions like a traditional IDE, but an agent pane on the side lets you instruct an AI in natural language.
By typing something like “generate a login page using React,” you spawn an agent who interprets the request, writes the code, and asks for confirmation before committing changes.

When you need more complex orchestration, the Manager View provides a mission-control dashboard that allows you to supervise multiple agents simultaneously.
For example, one agent might be implementing a backend API while another designs a user interface. The Manager View tracks each agent’s progress and surfacing of Artifacts, making it easy to approve or adjust plans.
Cross‑Surface Control
Unlike simple code completion tools, Antigravity’s agents can interact across the editor, terminal, and browser.
In one test project, I asked an agent to build a strong password generator app. The agent wrote the React components in the editor, executed “npm install” and “npm start” in the integrated terminal, and then opened a local browser window to verify the app’s UI.

This cross-surface ability mirrors the multi-surface integration described by both reviewers and Google’s own documentation. It means the AI can truly “do everything you would do on your machine”.
Artifacts and Feedback
Every major step the agent takes generates an Artifact. After creating the chat app’s login screen, the agent produced a Markdown report summarising the files it created, the commands it ran, and the test results.
I could annotate this report with comments—changing CSS values or pointing out missing fields—and the agent adjusted its plan accordingly.
Because artifacts include screenshots and sometimes screen recordings, it’s easy to verify that the agent’s work matches your expectations. This transparency represents a significant step toward building trust in an autonomous coding assistant.
Also Read: Landingsite.ai Review (2026): Build a Website in Minutes with AI?
Google Antigravity Features Walkthrough
1. Parallel Agents and Task Management
One of Antigravity’s strongest capabilities is the ability to run multiple agents concurrently. In one experiment, I created two agents in separate workspaces: the first built a React chat application using the Gemini API and OpenAI’s GPT-4 model. In contrast, the second designed an HTML mockup for a futuristic chat interface.
The agents worked in parallel; one wrote the code and installed dependencies while the other crafted an interface with a white and green palette. When Agent 1 reached a point where it needed to implement the mockup, I instructed a UI agent to integrate Agent 2’s output into the main project.
This hand‑off felt like directing interns rather than micromanaging a single assistant. The agents automatically generated Product Requirements Documents (PRDs) that explained their plans, and I could comment on these documents to modify pixel values or approve changes.
2. Automated Testing and Browser Simulation
Antigravity excels at automated testing thanks to its built‑in browser extension. After finishing the chat app, I asked the agent to write test cases and run them. It launched the application in a browser, performed clicks and input actions, and produced a test report listing which cases passed.
It also saved a video recording of the test session, which I could review later. This feature reduces the need for external testing frameworks, providing you with confidence that the AI-generated code is actually functional. However, the extension currently only supports Chrome, so users of Firefox or Safari must switch browsers.
3. Knowledge Base and Continuous Learning
A subtle but important feature is the knowledge base. Each agent retains snippets and lessons learned across sessions. When I later asked Antigravity to set up a Docker environment, it recalled the directory structure and environment variables from an earlier run, shortening the setup time.
Over the course of a week, I noticed that the agents became faster at routine tasks, such as creating Express servers or configuring ESLint, suggesting that the knowledge base genuinely improves productivity.
4. Multiple Model Support
By default, Antigravity uses Gemini 3 Pro, which Google claims outperforms GPT‑4 on code reasoning benchmarks. The platform also allows you to switch to Claude Sonnet 4.5 or GPT-OSS.
I tested the same task—building a REST API—using Gemini and Claude models. Gemini produced well‑structured code with accurate error handling, but occasionally over‑engineered the solution.
Claude’s output was more concise but sometimes missed edge cases. Switching models is straightforward through the settings menu; however, you cannot mix models within one agent, so comparisons require separate agents.
Also Read: Bolt.new Review: Hands-On with an AI IDE for Rapid Full-Stack Prototypes
Ease of Use & Learning Curve
Because Antigravity is based on VS Code, experienced developers will feel at home. The chat interface utilizes natural language, and the Manager View clearly explains each agent’s status.
However, the agent‑first paradigm demands a shift in mindset. Rather than manually editing code as you go, you often wait for an agent to produce a plan, review it, and then approve or adjust.
In early sessions, this process felt slower than simply typing, partly because the agents occasionally spent several minutes “thinking” before generating a plan. Over time, as I learned how to phrase prompts and when to intervene, the workflow became smoother.
For novices or non‑coders, the natural language interface could be empowering, but understanding the underlying code remains essential for safety and quality.
Performance & Output Quality
Speed and Rate Limits
During my tests, tasks ranged from near‑instant code suggestions to several minutes for more complex features. Google’s free individual plan offers unlimited command requests and generous rate limits that reset every five hours.
In practice, I never hit the quota on macOS, but a Windows‑using colleague exhausted his token allowance within minutes, possibly due to launch‑day bugs.
The agents sometimes paused with messages like “Agent execution terminated due to model provider overload,” a known issue reported by other early users.
Performance also depends on the chosen model; the Gemini 3 generally responds faster than the Claude Sonnet.
Quality of Code and Artifacts
Overall, the code generated by Antigravity’s agents was structurally sound and followed modern best practices. For example, the React components used hooks correctly and separated concerns.
The test cases covered typical user flows and included meaningful assertions. I still needed to refactor variable names or adjust styling, but the base implementation was usable.
The Artifacts were concise yet informative; they summarized what was done without overwhelming me with logs. In some cases, the agent misinterpreted a requirement—such as placing a button on the wrong side of a form—but a quick comment on the Artifact corrected the course.
Pricing & Value for Money
At launch, Antigravity’s individual plan is available for free. Users get access to Gemini 3 Pro, Claude Sonnet 4.5, and GPT‑OSS with generous quotas. The free tier includes unlimited autocompletions, command requests, and agent interactions.
Google resets quotas every five hours and says only “a tiny fraction” of power users will exceed them. There is no paid tier yet, but Google hints at potential paid features in the future.
Compared with paid alternatives like Cursor, which charges monthly fees, Antigravity offers remarkable value—assuming the preview bugs are ironed out.
Integrations, Devices & Support
Antigravity works as a desktop application on macOS, Windows, and Linux. Because it is built on VS Code, you can install most VS Code extensions and themes, and existing keybindings work out of the box.
The browser extension supports Chrome; integration with other browsers is not available yet. You can choose the AI backend (Gemini 3 Pro, Claude Sonnet, GPT‑OSS).
There is no mobile version, but Google suggests that remote collaboration features may arrive later. Support is limited to community forums and GitHub issues; there is no dedicated enterprise support for the preview.
Also Check: TypeScript to JavaScript Conversion Tool — Free Online AI Converter
Pros and Cons of Google Antigravity
Pros
- Parallel execution: Multiple agents can work simultaneously on different tasks, thereby improving productivity.
- Automated browser testing: Integrated testing and recording reduce reliance on external tools.
- Context sharing and knowledge base: Agents remember past actions and reuse knowledge.
- Generous free tier: Unlimited autocompletions and command requests with access to premium models.
- Transparency through Artifacts: Task summaries, screenshots, and reports make agent actions verifiable and transparent.
- Model choice: Ability to run Gemini 3, Claude Sonnet, or GPT‑OSS.
Cons
- Windows stability: Some early users have reported crashes and rapid quota exhaustion on Windows.
- Slower planning: Agents sometimes take minutes to generate plans, which can delay even simple tasks.
- Limited browser support: This feature is only compatible with Chrome; users of Firefox or Safari must switch to Chrome for optimal functionality.
- Learning curve: Adopting the agent-first workflow requires patience and trust in the AI.
Google Antigravity Alternatives
1. Cursor (Cursor 2.0)
Cursor is another AI‑native IDE focused on speed. It operates mainly in the background, generating code and verifying it without showing every step. According to a comparison by Geeky Gadgets, Cursor emphasizes speed, while Antigravity prioritizes transparency and user control.
In my tests, Cursor produced code faster but offered less insight into its reasoning. Antigravity’s artifacts and Manager View made it easier to understand and correct the AI’s work.
2. Windsurf Editor
Windsurf is a VS Code fork that inspired Antigravity; Google acquired the Windsurf team in mid‑2025. Early users note that Antigravity feels like Windsurf, with deeper integration of agents and artifacts.
Windsurf focuses on using a single agent embedded in the editor, whereas Antigravity adds the Manager View for orchestrating multiple agents and supports a broader range of models. If you liked Windsurf’s interface, Antigravity offers a more ambitious extension of that concept.
3. GitHub Copilot
GitHub Copilot remains the most widely used AI code assistant. It offers autocomplete and inline suggestions, but cannot run commands or interact with the browser. Copilot requires external test frameworks and manual execution, whereas Antigravity’s agents can build, run, and test complete applications.
Copilot is simpler and more stable, making it ideal for quick snippets. Antigravity is better suited for full‑stack tasks and those who want deeper collaboration with AI.
Blackbox.ai and Other Agentic IDEs
Other alternatives, such as Blackbox.ai, Coze, and Jotform AI Agents, provide agentic coding or customer service features.
Blackbox.ai offers code completion, app building, and reasoning capabilities, but it is web‑based and lacks Antigravity’s mission‑control dashboard.
Coze and Jotform AI Agents are more focused on customer service bots than full‑stack development.
In summary, Antigravity distinguishes itself by offering multi‑agent orchestration in a local IDE with cross‑surface control.
Final Verdict
After a week of hands‑on use, I believe Google Antigravity is an ambitious leap toward an agent‑first development paradigm. For solo developers and small teams building web apps, Antigravity can boost productivity by automating mundane tasks.
It is less suitable for mission‑critical or highly sensitive projects until privacy and security policies are clarified.
Google Antigravity’s ability to coordinate multiple agents, generate verifiable Artifacts, and execute complete workflows—from coding through testing—distinguishes it from current AI assistants.
The free tier makes it accessible, and the option to choose between Gemini 3, Claude Sonnet, and GPT‑OSS models adds flexibility.
Rating: 4 out of 5 for innovation and potential.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What problem does Antigravity solve?
It aims to eliminate tedious coding and testing tasks by letting AI agents plan, write, run, and verify code across the editor, terminal, and browser.
2. Is Google Antigravity free?
Yes. The individual preview plan is free, offering access to Gemini 3 Pro, Claude Sonnet 4.5, and GPT‑OSS with generous rate limits that reset every five hours.
3. Which models does Antigravity support?
Out of the box, it uses Google’s Gemini 3 Pro, but it also supports Anthropic’s Claude Sonnet 4.5 and the open‑source GPT‑OSS.
