Artificial intelligence has moved beyond flashy demos and into the daily workflows of software development. Today’s AI coding assistants do much more than autocomplete functions; they can explain existing code, generate unit tests, refactor multiple files, and even act as autonomous agents that manage pull requests.
Used thoughtfully, these tools can cut development time and help you focus on design and architecture. Used blindly, they can introduce subtle bugs or hidden license issues.
In this article…
This guide approaches AI assistants from a practitioner’s perspective. Rather than rehashing hype, it explains why specific features matter, offers practical tips, and compares ten of the most capable tools available.
Choosing the Right AI-Powered Coding Assistants
Before diving into specific tools, consider how you’ll use them. There are three broad categories:
- Integrated assistants live inside your IDE (VS Code, JetBrains, Neovim, etc.) and offer real‑time completions and chat. Examples include GitHub Copilot, Tabnine, and JetBrains AI Assistant.
- Agentic assistants can autonomously execute multi‑step tasks such as generating entire features, refactoring across files, or pushing draft pull requests. GitHub Copilot’s new Agent Mode and Amazon Q Developer’s/dev agent fall into this category.
- Self‑hosted frameworks allow you to bring your own model and keep code on premises. Open‑source projects like Aider, Continue, and Cline exemplify this approach.
When evaluating any assistant, pay attention to:
- Language support: Some tools excel in popular languages like JavaScript or Python, while others support dozens of languages.
- Privacy and deployment: Do you need a cloud service or an on‑premise option? Tools like Tabnine offer on‑premise and even air‑gapped deployments.
- Feature set: Compare autocomplete, chat, test generation, documentation, refactoring, and agentic capabilities. Many assistants specialise in one or two areas.
- Pricing: Free tiers may suffice for individual use, but team plans often unlock more context or agent modes. Consider usage‑based pricing for heavy use.
With those criteria in mind, let’s examine ten leading AI‑powered coding assistants and how they can fit into your workflow.
Also Check: 5 Best VS Code AI Extensions for Smarter Coding (Free Tools)
1. GitHub Copilot – the mainstream pair programmer
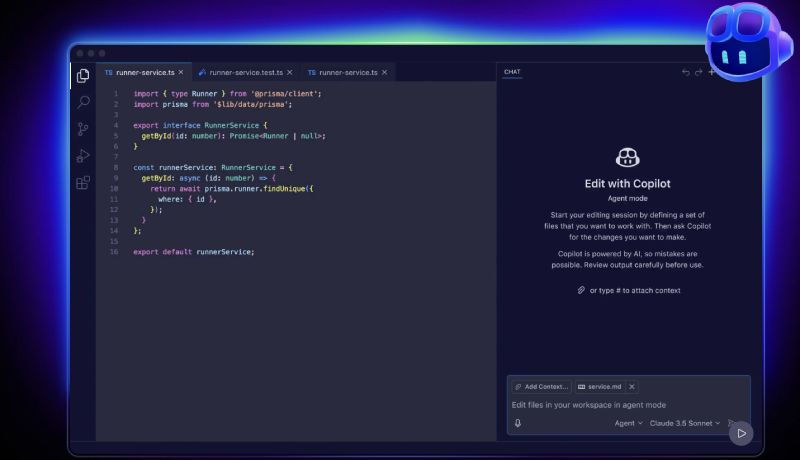
GitHub Copilot remains the most widely adopted AI assistant thanks to tight integration with Visual Studio Code, JetBrains IDEs, and Neovim.
Born from a collaboration between GitHub, OpenAI, and Microsoft, Copilot’s model is trained on billions of lines of open‑source code and can provide context‑aware completions and explanations.
According to GitHub, developers using Copilot report a 75% higher sense of job satisfaction and complete tasks up to 55% faster.
Key features:
- Real‑time code completion and chat. Copilot suggests entire lines or functions as you type and offers a chat interface for asking questions about your code’s behavior or unknown APIs. Its suggestions improve when you provide comments and meaningful variable names, so treat it like a junior pair programmer.
- Agent Mode. A notable 2025 addition is an autonomous agent that can handle complex tasks such as creating a new feature, writing tests, refactoring code, and iterating until the build passes. The agent reads your repository, plans the changes, executes them, and creates a draft pull request for your review.
- Model and privacy controls. Copilot lets you block suggestions that match public code snippets, avoiding accidental license violations. Business and Enterprise plans include policy settings to manage code retention and compliance.
Limitations:
Copilot’s strength is its general‑purpose nature and smooth IDE integration, but it comes with trade‑offs. Because it runs in the cloud, your code is sent to Microsoft/OpenAI’s servers unless you use enterprise self‑hosting.
Code quality varies across languages – JavaScript and Python perform better than less‑represented languages.
Pricing starts at free (with limited completions) and ranges up to $39 per user per month for full agent capabilities. For quick autocompletion and mainstream development, Copilot remains a tough competitor to beat.
2. Amazon Q Developer – multi‑agent assistance in the AWS ecosystem
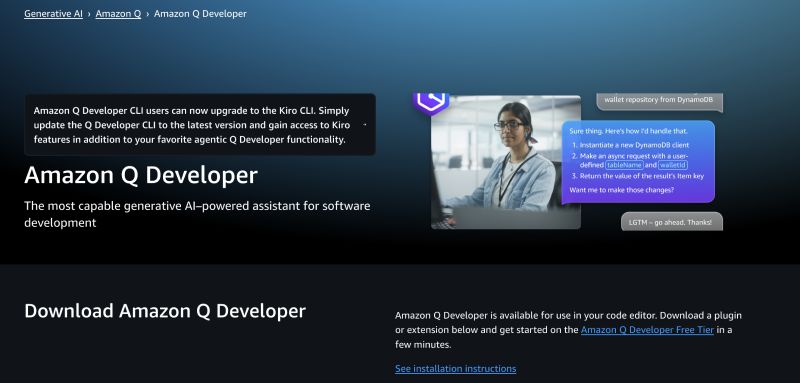
Announced in late 2024 and rapidly iterated through 2025, Amazon Q Developer is AWS’s answer to Copilot. Unlike Amazon’s earlier CodeWhisperer, Q Developer includes several specialised agents.
A /dev agent can implement features across multiple files, a /doc agent generates diagrams and documentation, and a /review agent automates code review. It integrates directly with IDEs like VS Code and JetBrains and provides a CLI for terminal workflows.
Key features:
- Natural‑language prompts across more than 25 languages. Q Developer generates full functions or classes from conversational descriptions and supports JavaScript, Python, Java, C#, Go, and more.
- Documentation and test generation. It can automatically write documentation, README files, and unit tests. The tool also explains code in plain language, making it useful when inheriting unfamiliar repositories.
- Security scanning. Q Developer scans for vulnerabilities during generation and offers actionable fixes, appealing to enterprises in regulated industries.
- Real‑world adoption metrics. Medium reports that teams at BT Group and National Australia Bank have seen 37 % and 50 % of Q‑generated code accepted into production, respectively, suggesting maturity beyond a demo stage.
Limitations:
Q Developer shines when you’re already invested in AWS. It leverages AWS’s identity and access management and can be configured to avoid retaining your code. However, it’s a closed‑source SaaS product with usage‑based pricing, and using the CLI or agent modes may incur additional costs.
3. Google Gemini Code Assist (Duet AI) – context with citations
Google’s Gemini Code Assist, previously known as Duet AI for Developers, became generally available in 2024 and continues to evolve.
Powered by the Gemini 2.5 model, it provides AI assistance in Cloud Shell, Cloud Workstations, and IDEs, including Google Antigravity, VS Code, JetBrains, and Android Studio. Gemini distinguishes itself by citing the origin of code suggestions and offering a generous free tier.
Key features:
- Code completion and generation with citations: Gemini can suggest code snippets, refactor functions, and generate entire modules. It provides citations linking to documentation or code samples that inspired the suggestion, helping developers verify output and learn.
- Chat and smart actions: Developers can ask how a piece of code works or request tests and documentation directly from the IDE. Gemini can transform selected code and exclude files via .aiexclude or .gitignore rules.
- Generous free tier: Google offers high monthly limits for individual developers; paid enterprise plans add admin controls and advanced context windows.
Considerations:
Gemini Code Assist appeals to developers who value citations and integration with Google Cloud. Its suggestions are strongest for languages popular in Google’s ecosystem (Kotlin, Go, Python) and mobile development through Android Studio.
Also Read: Google Gemini 2.5 vs GPT-4: Which AI Model Should You Choose in 2025?
4. Tabnine – privacy‑first completions and custom models
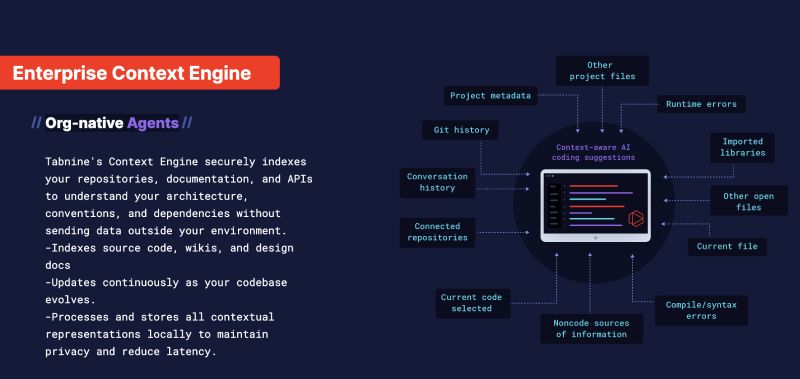
Tabnine has long positioned itself as the privacy‑centric alternative to Copilot. It runs on proprietary models trained on permissively licensed code and offers on‑premise, VPC, or air‑gapped deployment options. Tabnine integrates with more than 30 languages and all major IDEs.
Key features:
- Personalised suggestions. Tabnine’s Enterprise Context Engine learns your team’s architecture and coding standards to generate context‑aware completions. You can even train custom models on your codebase, ensuring suggestions match internal patterns.
- Multi‑model support. Users can choose between Tabnine’s proprietary models or third‑party models and adjust suggestions accordingly.
- Flexible deployment. For security‑conscious teams, Tabnine offers SaaS, VPC, on‑premises, and air‑gapped installations. This means code never leaves your environment if you don’t want it to.
Considerations:
Tabnine excels at privacy and customisability but lacks some of the advanced agentic features of Copilot or Amazon Q.
The free version offers basic completions but restricts access to advanced functions. Its suggestions may feel less intuitive for beginners compared to Copilot. For organizations concerned about intellectual property leakage, Tabnine is a compelling option.
5. JetBrains AI Assistant – deep IDE integration with multiple models
JetBrains, the company behind IntelliJ IDEA and PyCharm, introduced its own AI assistant in 2023 and has continuously expanded it.
It supports code completion, natural‑language code generation, refactorings, documentation creation, and unit test generation across multiple JetBrains products.
Key features:
- Smart completion and next edit suggestions: The assistant predicts entire blocks of code and even suggests the next logical edit based on context
- Natural‑language prompts and chat: You can describe a desired function in plain English, and the assistant will generate it, complete with tests and documentation. A chat interface answers questions about frameworks and APIs, similar to Copilot’s chat.
- Multiple LLM back‑ends: JetBrains allows you to choose between models from OpenAI, Google (Gemini), Anthropi,c and its own Mellum model, or connect to a local model through the Ollama integration. This flexibility lets organizations pick a model that meets privacy and cost requirements.
- Smart apply and commit messages: Generated code can be inserted with one click using Smart Apply, ensuring proper formatting and imports. The assistant also writes commit messages based on diffs.
Limitations to consider:
JetBrains AI Assistant is powerful but only works within JetBrains IDEs. It’s free while in technical preview, but pricing and usage limits may change as it matures.
If you’re heavily invested in IntelliJ or Android Studio, it delivers a seamless experience; otherwise, cross‑IDE options like Copilot may be more flexible.
Also Read: Landingsite.ai Review (2026): Build a Website in Minutes with AI?
6. Replit AI – build and debug entire projects in the browser

Replit’s browser‑based IDE has long emphasised ease of use and collaboration. Replit AI builds on that with two components: the Agent and the Assistant.
According to Replit’s documentation, the Agent can generate entire applications based on natural-language descriptions, while the Assistant explains code and helps with debugging. This dual approach allows users to build full‑stack applications or fix bugs through conversation.
Key features:
- Project generation. You can ask Replit Agent to “build a to‑do app with user authentication,” and it will scaffold the project, write code, and configure dependencies.
- AI debugger and code explanation. The Assistant can pinpoint bugs, suggest fixes, and describe how unfamiliar code works, making it useful for learning and legacy projects.
- Seamless cloud environment. Because everything runs in the browser, there is no local setup; your code, terminal, and hosting are integrated. Collaboration features enable you to pair program with teammates in real-time.
Limitations:
Replit AI is great for rapid prototyping, hackathons, and educational projects. However, its context window is currently limited – the assistant sometimes loses track of earlier conversation threads.
It is also tied to Replit’s platform; projects built there may require migration work to move to a self‑hosted environment.
Pricing is usage‑based with a free tier; heavy use of the agent incurs additional compute credits.
Suggested Read: 200+ AI Statistics You Need to Know Before 2026
7. Windsurf – free completions with privacy options
Codeium burst onto the scene as an unlimited free code completion tool supporting over 70 languages and numerous IDEs.
It positions itself as a privacy‑friendly alternative to Copilot; code processing can run locally, and the company claims no training on customer code.
In 2024, Codeium launched Windsurf, an AI‑first IDE that integrates these capabilities directly into the editor.
Key features:
- Unlimited completions and chat: Unlike most tools, Codeium’s free tier offers unlimited code suggestions across multiple languages and supports an interactive chat that understands project context.
- Multi‑IDE integration and translation: It works with Visual Studio Code, JetBrains, Vim, and cloud platforms. The assistant can generate documentation, translate code between languages, and detect errors in real time.
- Privacy‑first architecture: Codeium runs models locally where possible and does not train on your code. Enterprise customers can self‑host the model within their own infrastructure.
Limitations:
According to reviewers, Codeium’s context understanding is strong for small to medium projects but can struggle in large, complex codebases.
Advanced agentic features like multi‑file refactoring are limited compared with Copilot’s Agent Mode. Nonetheless, its free pricing and privacy stance make it attractive for individuals and budget‑conscious teams.
8. Sourcegraph Cody – search‑first context and codebase awareness
Sourcegraph, known for its code search platform, built Cody to be a context‑aware coding assistant. Rather than generating code blindly, Cody first searches your entire repository to assemble relevant snippets and documentation. It then uses retrieval‑augmented generation to craft responses.
Key features:
- Codebase‑aware chat and autocomplete. Cody’s chat interface can answer questions about your codebase and suggest context‑enhanced completions. Because it indexes your repository, it understands module boundaries and can link to relevant files.
- Command library and smart apply. Predefined commands, such as “explain this file,” “generate unit tests” or “migrate to TypeScript,” speed up common tasks. When Cody proposes edits, Smart Apply inserts them directly into your code, handling diffs properly.
- Multi‑model support. Cody can work with different LLMs and is accessible as a plugin for VS Code, JetBrains, and in Sourcegraph Cloud.
Limitations:
Cody’s search‑first design improves accuracy but introduces latency; it takes longer to gather context before generating a response.
It excels in large monorepos where context is crucial, and its strengths lie in refactoring and documentation.
Pricing starts with a generous free tier on Sourcegraph Cloud; enterprise plans allow self‑hosting and model choice.
9. Cursor – an AI‑first IDE with composer and agent modes
Cursor is a fork of Visual Studio Code that integrates AI deeply into the editor. Beyond autocomplete, it offers a Composer Mode for chat‑based multi‑file changes and an Agent Mode that can autonomously implement high‑level tasks.
Cursor also introduces a .cursorrules file for specifying style guidelines and controlling how the agent operates.
Key features:
- Composer and Agent modes: Composer Mode allows you to chat about a change and then manually apply the generated diff. Agent Mode goes further, executing tasks autonomously, editing multiple files, and generating commit messages.
- Integrated debugging and multi‑tabbing: Cursor provides inline debugging hints and the ability to open multiple AI tabs when iterating on complex problems.
- Governance via .cursorrules: You can define patterns the agent should follow, specify files to ignore, and enforce coding styles, giving you more control over the AI’s behavior.
Limitations:
Cursor’s AI services are closed source and rely on cloud inference. It is subscription‑based and targeted at power users who want an AI‑native IDE rather than a plug‑in.
For developers comfortable with VS Code, the learning curve is minimal, but some may prefer tools that integrate with existing IDEs rather than replacing them.
10. Bolt.new – natural‑language web development in the browser
Bolt.new, created by StackBlitz, leverages WebContainers to enable full‑stack web development entirely in the browser. It allows you to prompt, run, edit, and deploy applications using natural language.
Bolt.new is domain‑specific – it excels at quickly scaffolding React, Vue, Next.js, and other JavaScript frameworks.
Key features:
- Full‑stack project scaffolding. You can describe an app (“build a blog with authentication and comments”) and Bolt.new will generate a working project, install packages, and configure routing.
- Live editing and one‑click deployment. The interface lets you edit code, see changes instantly, and deploy to hosting services or Vercel subdomains with a click.
- Framework coverage. It supports popular frameworks like React, Vue, Next.js, Angular, and Svelte, and can integrate with Supabase or other back‑ends.
Some limitations:
Bolt.new is ideal for quickly prototyping web apps or learning frameworks. It’s less suitable for back‑end heavy or non‑JavaScript projects.
Pricing tiers include Free (limited token use), Starter, Pro, and Enterprise. Because it’s a hosted service, you’re tied to StackBlitz’s ecosystem, so consider export options if you plan to host elsewhere.
Wrapping up and looking ahead
AI‑powered coding assistants are no longer novelty tools; they’re becoming integral to modern software development. This article compared ten assistants across cloud, desktop and browser environments, emphasising real‑world features over marketing hype.
GitHub Copilot continues to set the baseline with broad language support and a new agent mode, while Amazon Q Developer and Google Gemini Code Assist differentiate with multi‑agent orchestration and citations.
Tabnine and Codeium appeal to privacy‑conscious teams, JetBrains and Cursor offer deep IDE integration, and Replit AI and Bolt.new cater to cloud‑native workflows. Sourcegraph Cody stands out for its search‑first approach.
No single assistant is perfect. Autocomplete tools can hallucinate, agents may overlook project nuances, and closed‑source services raise privacy concerns. The best approach is to treat AI as an intelligent collaborator, not a replacement.
As large language models improve and more context becomes available, expect assistants to move from suggestive helpers to reliable co‑developers that understand your entire system and contribute meaningfully to design and architecture.
